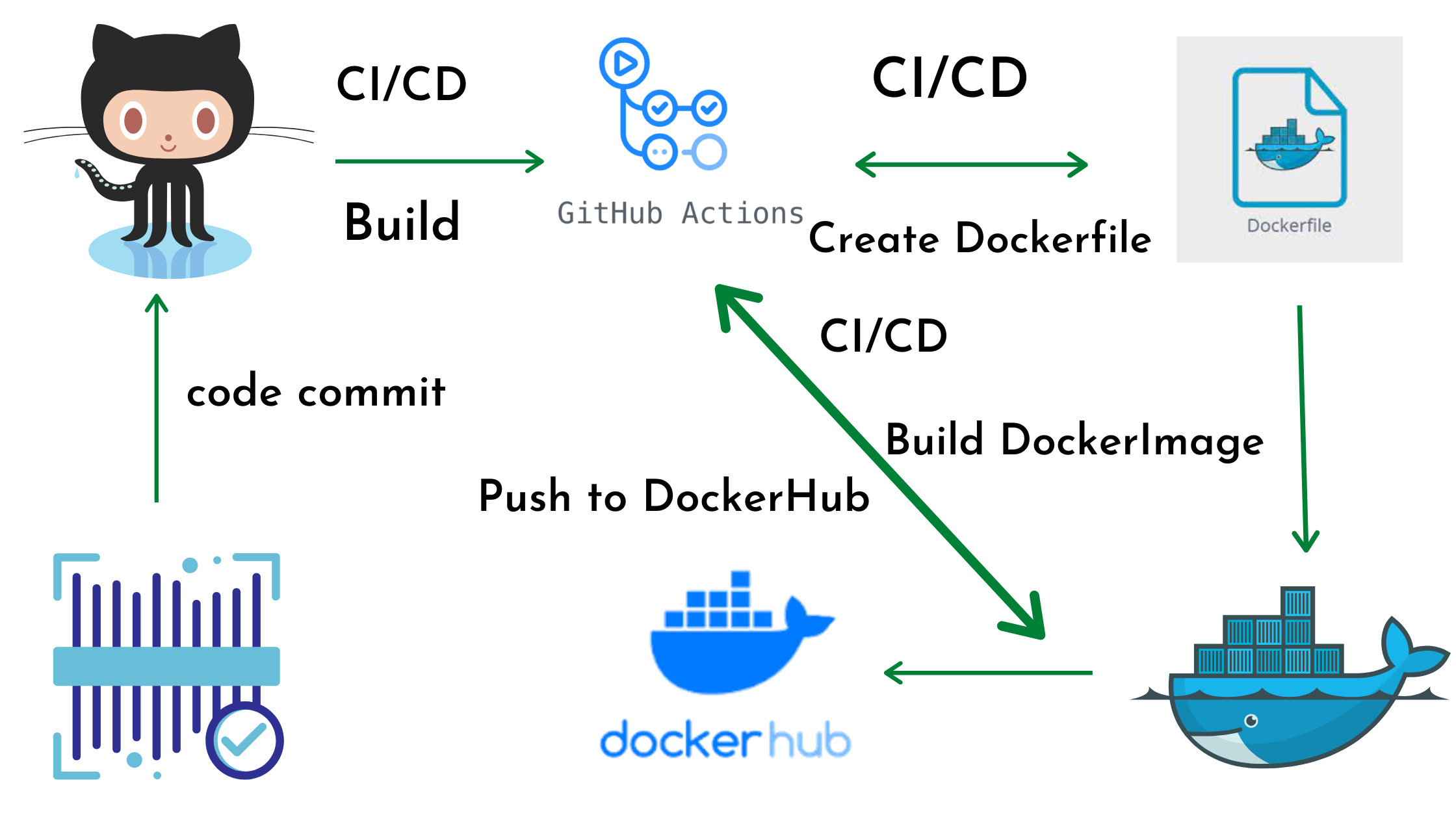
In this article we are going to cover GitHub Actions Tutorial with Practicals. What is GitHub Actions ? GitHub Actions is a built-in CI/CD (continuous integration and continuous delivery) platform that lets you automate tasks within your software development lifecycle. In layman’s terms, it automates repetitive tasks you typically do throughout the development process. What GitHub Actions can do ? GitHub Actions Components What is Workflow in GitHub Actions? Components of Workflow in GitHub Actions? Events: These are the triggers that initiate the workflow. Common events include: Jobs: Steps: Each job consists of a series of steps, which are the individual commands that make up the job. Steps can include: Benefits of Workflow in GitHub Actions? How to Create Workflow in GitHub Actions? 1. Setting Up the Directory: If it doesn’t exist yet, create a directory named .github/workflows within your repository. This is where GitHub Actions will look for workflow files. 2. Creating the Workflow File: 3. Defining the Workflow: Explanation of the workflow Template: <Your workflow name>: Replace this with a descriptive name for your workflow. <Event triggers>: Specify the events that will trigger the workflow execution. This could be push (to a specific branch), pull_request (actions), or a schedule (e.g., daily). Refer to the Actions documentation for all event options https://github.com/marketplace/actions/google-docs-to-github. <Job name>: Define names for each job within the workflow. <Runner operating system>: Specify the operating system (e.g., ubuntu-latest, windows-latest) for the virtual machine (runner) that will execute the job. <steps>: This section lists the individual commands to be executed for each job. You can use pre-built actions from the marketplace or define your own custom commands. 4. Adding Steps to the Workflow: Under the steps section for each job, define the commands you want to run. You can use pre-built actions by specifying the action name and version (e.g., uses: actions/checkout@v3). Refer to the marketplace for available actions on GitHub Actions official page. Alternatively, you can define your own shell commands directly (e.g., run: npm install). 5. Committing and Pushing the Workflow: Once you’ve defined your workflow in the YAML file, commit the changes to your repository. Push the changes to your remote repository on GitHub. Example: 6. Run GitHub Actions workflow On GitHub.com, navigate to the main page of the repository. under your repository name, click Actions. In the left sidebar, click the name of the workflow you want to run. Above the list of workflow runs, click the Run workflow button. Select the Branch dropdown menu and click a branch to run the workflow on. If the workflow requires input, fill in the fields. Click Run workflow. Conclusion: In this article we have covered GitHub Actions Tutorial with Practicals. Related Articles: What is Git and GitHub?